Important links
Abstract
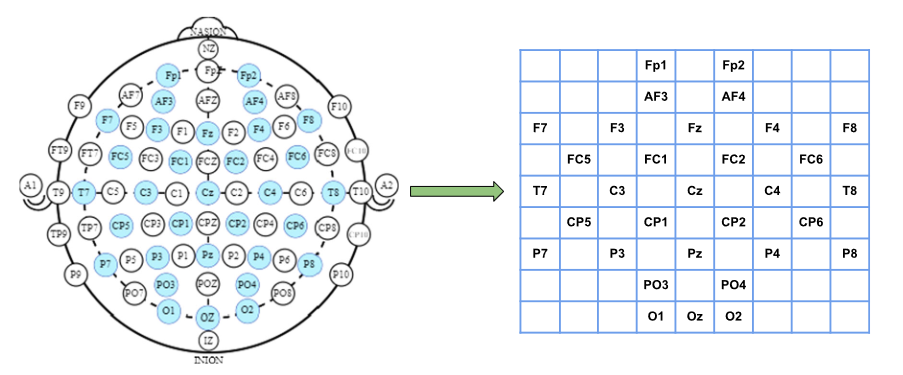
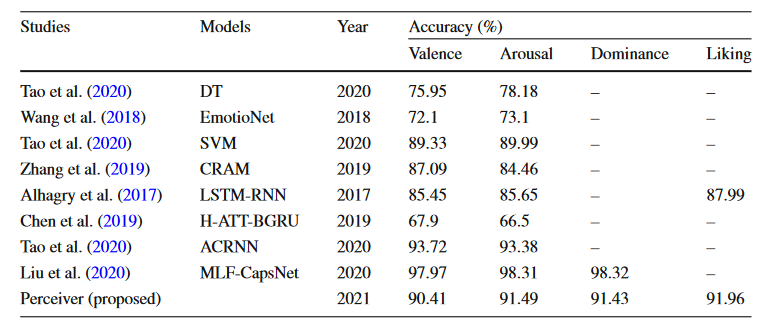
Emotions play an important role in human cognition and are commonly associated with perception, logical decision making, human interaction, and intelligence. Emotion and stress detection is an emerging topic of interest and importance in the research community. With the availability of portable, cheap, and reliable sensor devices, researchers are opting to use physiological signals for emotion classification as they are more prone to human deception, as compared to audiovisual signals. In recent years, deep neural networks have gained popularity and have inspired new ideas for emotion recognition based on electroencephalogram (EEG) signals. Recently, widespread use of transformer-based architectures has been observed, providing state-of-the-art results in several domains, from natural language processing to computer vision, and object detection. In this work, we investigate the effectiveness and accuracy of a novel transformer-based architecture, called perceiver, which claims to be able to handle inputs from any modality, be it an image, audio, or video. We utilize the perceiver architecture on raw EEG signals taken from one of the most widely used publicly available EEG-based emotion recognition datasets, i.e., DEAP, and compare its results with some of the best performing models in the domain.
Important figures
Citation
@article{aadamEmoPerceptEEGbasedEmotion2022,
title = {EmoPercept: EEG-based Emotion Classification through Perceiver},
author = {{Aadam} and Tubaishat, Abdallah and {Al-Obeidat}, Feras and Halim, Zahid and Waqas, Muhammad and Qayum, Fawad},
year = {2022},
journal = {Soft Computing},
issn = {1433-7479},
doi = {10.1007/s00500-021-06578-4},
}